Essential Maintenance Metrics Every Planner Needs to Know
Get Free Guide
While cloud-based maintenance solutions have become an industry standard, there are situations in which on-premise CMMS can be a better match for a company’s specific requirements.
As a vendor that offers both cloud and on-premise deployment, we are in a unique position to objectively discuss both sides of this story.
How does on-premise CMMS software work?
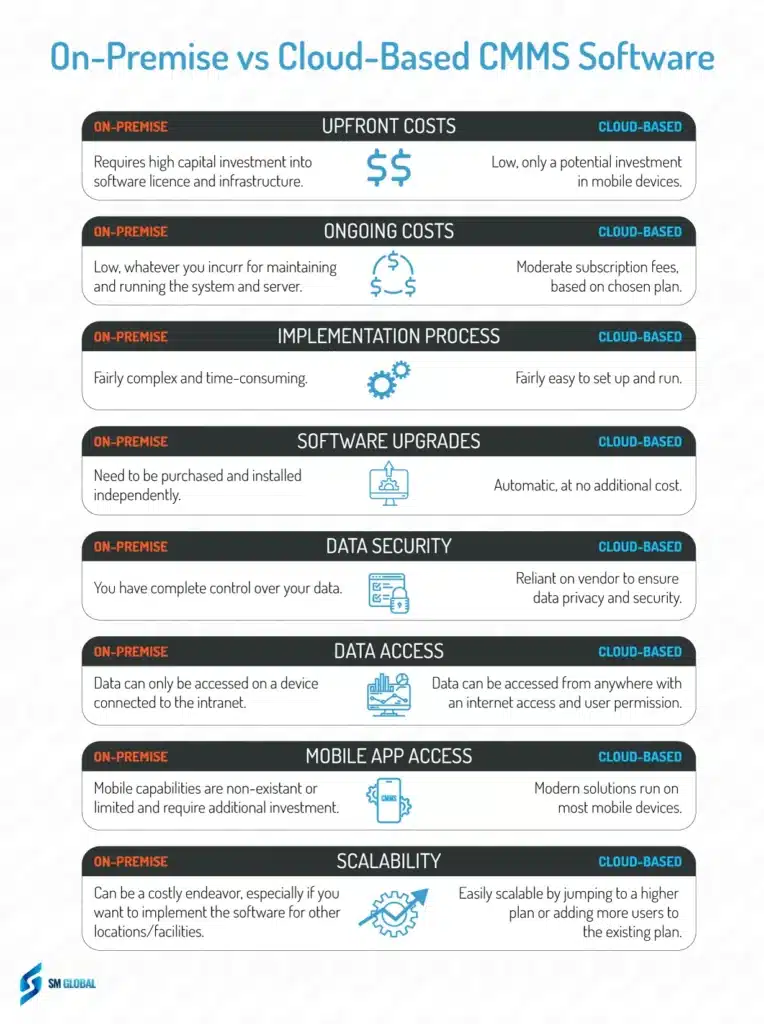
On-premise CMMS operates from a company’s internal servers, requiring the infrastructure and resources required to support and maintain the system locally. You basically buy the license from a specific vendor and install their CMMS on your internal servers.
There are a couple of specific situations in which on-premise CMMS excels:
- All the data is stored within the company’s premises, making it the preferred option for organizations with stringent security policies or those that need complex, custom integrations.
- It is particularly well-suited for organizations that have well-established IT infrastructure and a preference for capital expenditure over operational expenditure.
Advantages of implementing on-premise CMMS software
- More control over your data: Organizations have complete control over their data, which stays in-house, potentially offering more robust security and minimizing 3rd party data access.
- Better customization: On-premise CMMS offers greater flexibility for customization. You can make changes to the software to meet specific organizational needs and integrate with existing systems.
- Less connectivity issues: Reduced dependency on internet connectivity, as the system can function efficiently without a connection to external servers. You still need to set up a reliable intranet though.
- Easier regulatory compliance: Using on-premise CMMS deployment may be easier if you need to comply with stringent industry regulations and standards regarding data handling and storage, especially in sectors like healthcare and finance.
- More stable costs: There is a predictable cost structure where companies are not bound by the recurring (and changing) subscription fees that are characteristic of cloud-based systems.
Disadvantages of on-premise CMMS deployment
- High initial costs: Higher upfront costs due to necessary investments in server hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure.
- More hassle with maintenance and upkeep: Requires an in-house IT team to manage, maintain, and troubleshoot the system, which can spend substantial internal resources.
- Scalability issues: Scaling the system to accommodate business growth can be challenging and might require additional investments in hardware and software.
- Limited data access: Remote access to the system might be limited or require additional setup, potentially hampering the flexibility of operations, especially in remote or geographically dispersed teams.
- Update delays: Software updates and patches are not as frequent or as easy to deploy, potentially leaving the system with outdated features or vulnerable to security risks.
- Data recovery problems: Developing a robust disaster recovery plan is crucial, as data loss can be more significant when compared to cloud solutions which usually have a built-in redundancy and automatic backup.
How does cloud-based deployment work?
A cloud-based CMMS is running on servers hosted by a third-party provider. This deployment model ensures that all system data and applications are stored on secure, remote servers, and users can access the system from anywhere, provided they have an internet connection.
To continue using the software, an organization pays a monthly subscription fee, which usually scales up or down with the number of users. In return, the vendor takes responsibility for all backend processes, including system updates, maintenance, and security protocols, minimizing the IT burden on the organization utilizing the system.
These days, most organizations opt for cloud-based CMMS solutions as they are easier to implement and scale. A modern, cloud-based CMMS software can be used to manage asset and maintenance work in virtually any industry.
The benefits of using cloud-based solutions
- Ease of access: Allows for easy remote access to the software from any location with an internet connection. Extremely helpful for maintenance managers and technicians performing off-site and field work.
- Low initial costs: Lower upfront costs, as there is no need for substantial investment in IT infrastructure and department. Technicians only need an average smartphone/tablet and a stable internet connection to fully utilize the software.
- Quick implementation: Faster and simpler implementation process compared to on-premise solutions, enabling businesses to get up and running quickly.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to accommodate business growth or contraction, without any operational disruptions.
- Automatic updates: The CMMS provider routinely manages software updates and improvements, ensuring users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
- Data backup: Cloud-based CMMS comes with robust backup and recovery features, safeguarding data against potential loss due to system failures, cyber attacks, human mistake, or other disasters.
The disadvantages of cloud-based maintenance software
- Internet dependency: Some cloud-based solutions do not offer an “offline mode”, which means that you simply can’t use the system in remote locations with poor internet connection.
- Data security concerns: Since the data is stored on external servers, you have to trust your provider to follow data privacy and security best practices.
- Limited customization: Cloud-based CMMS generally offers less customization options compared to on-premise solutions, as changes need to be consistent across all users of their product.
- Recurring costs: The subscription-based pricing model means businesses will incur ongoing costs to use the service. You might also need to switch to a higher-tiered plan to access more advanced features, significantly increasing your monthly fee.
- Potential downtime: Possible downtime due to server issues from the provider’s end, which is beyond your control.
- Potential integration challenges: Companies may encounter difficulties in integrating with existing in-house systems, especially if they are older or less common.
On-premise CMMS vs cloud-based CMMS: Final considerations
While both approaches are viable for most companies, there is a strong trend in favor of cloud-based solutions. Its ease of use and convenience is hard to beat. While we listed many potential disadvantages of using cloud-based maintenance software, the reality is that they are not a stumbling block for most organizations.
Despite all of that, on-premise solutions still have their place for organizations with specific security and customization requirements.
Ultimately, this should be a strategic decision that takes into account all of the benefits and potential limitations of each deployment model.
If you need additional help, download our free CMMS Selection Guide and find the best CMMS package for your needs.
Free CMMS Software Selection GuideEssential Maintenance Metrics Every Planner Needs to Know
Get Free Guide
